How AMVUTTRA® Works
Suppress TTR production at the source with AMVUTTRA1
AMVUTTRA addresses the underlying cause of ATTR‑CM and hATTR‑PN with rapid knockdown of TTR1-3
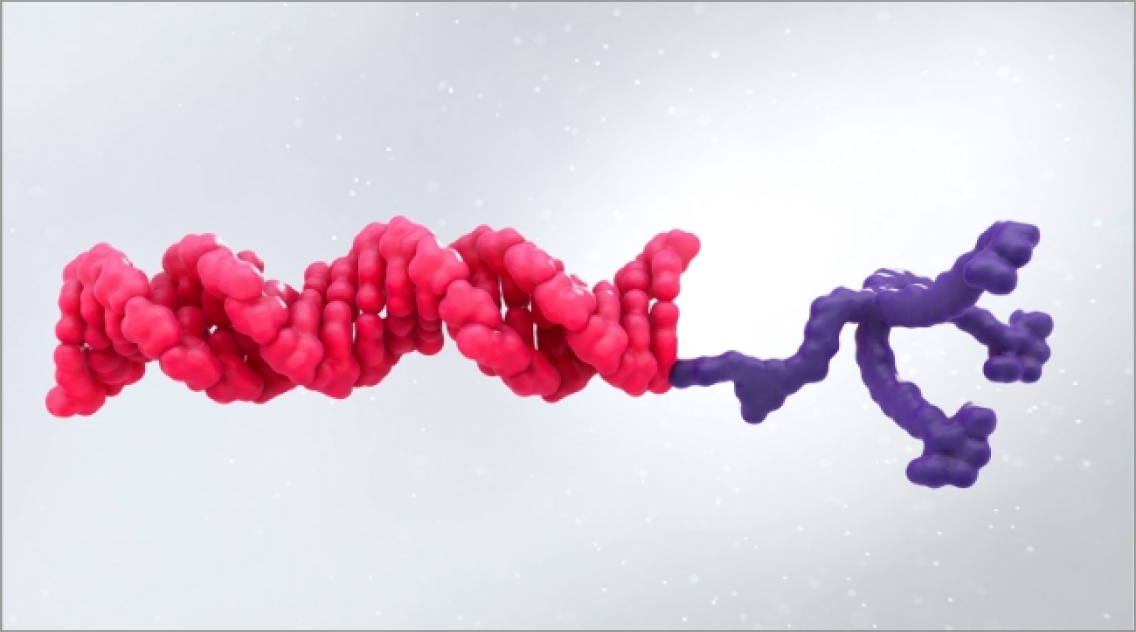
ATTR is a multisystem disease caused by pathogenic TTR4-7
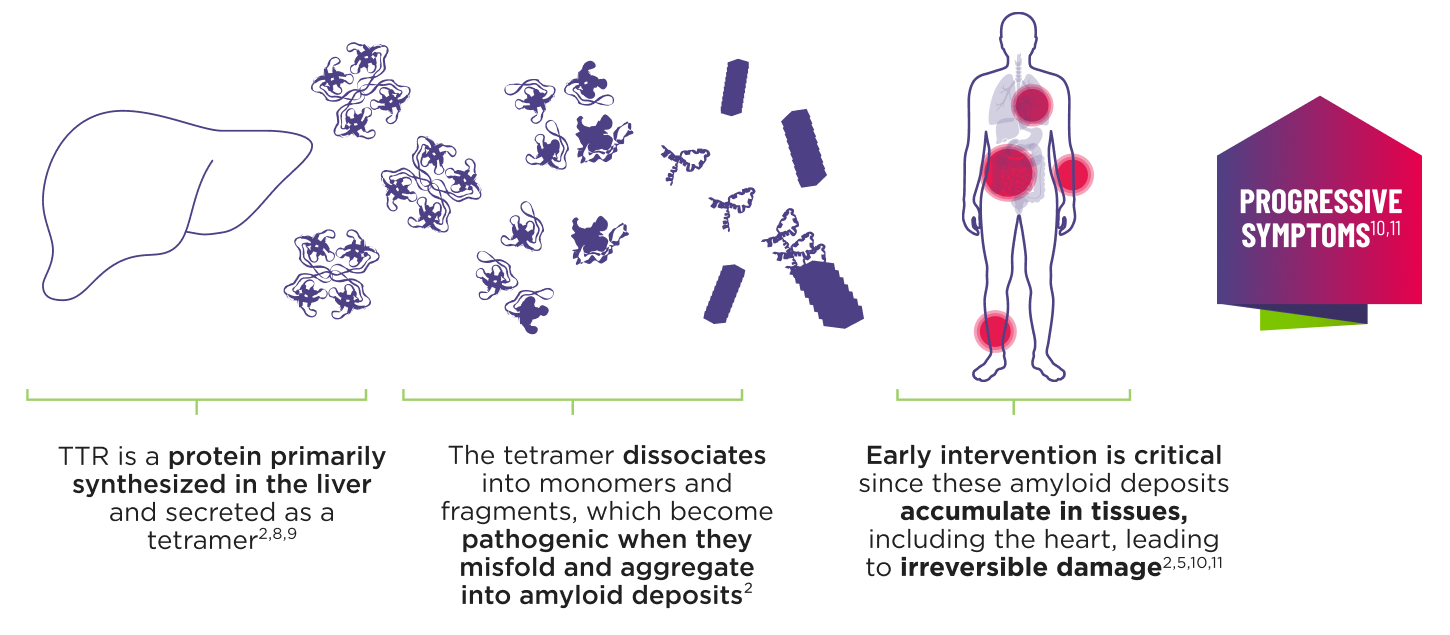
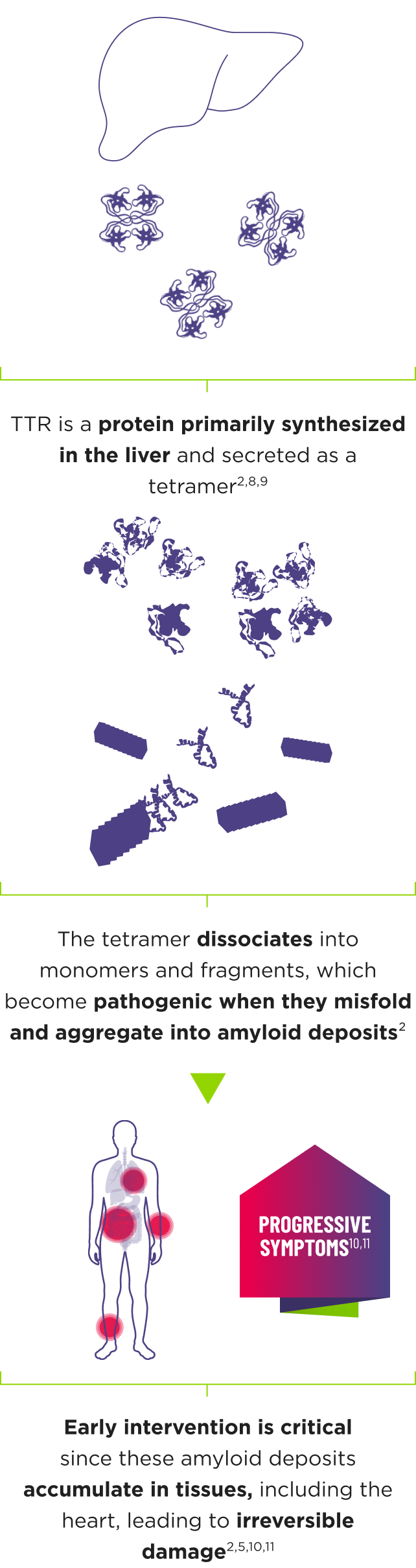
ATTR is a multisystem disease caused by pathogenic TTR4-7
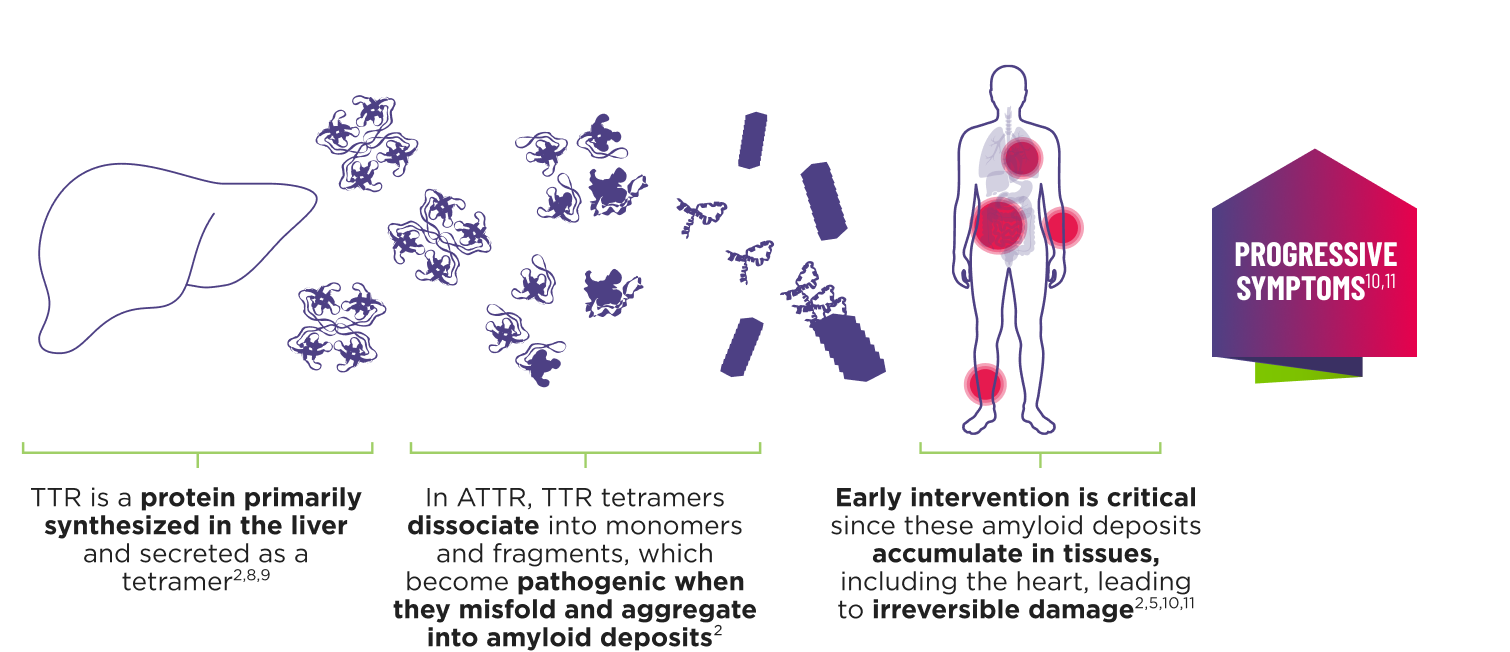
Cardiomyopathy is a common manifestation of ATTR (ATTR‑CM) that may lead to heart failure; musculoskeletal manifestations, polyneuropathy, and other symptoms may also present.5,7,12
mRNA=messenger RNA; RNAi=ribonucleic acid interference; TTR=transthyretin.
- Transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis (ATTR) is an underdiagnosed, progressive, debilitating, and fatal disease13
- Patients with ATTR may be diagnosed 3 to 8 years after symptom onset13-15
- If left untreated, the median survival for patients with ATTR is 2.5 to 5.5 years post- diagnosis16-19
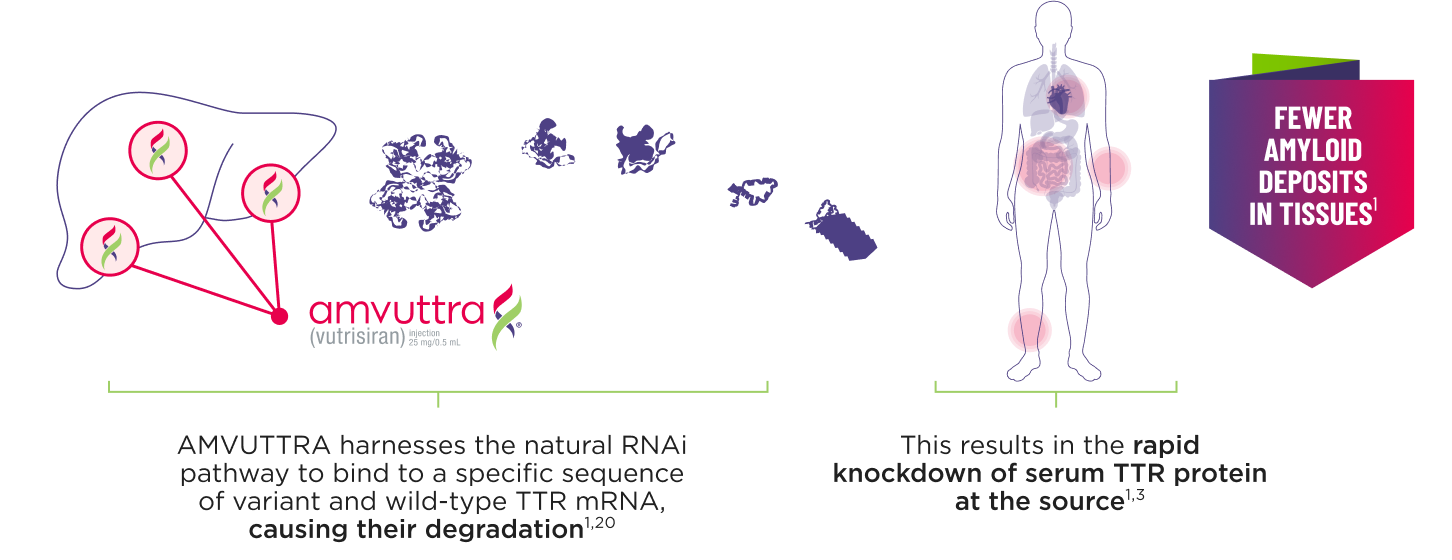
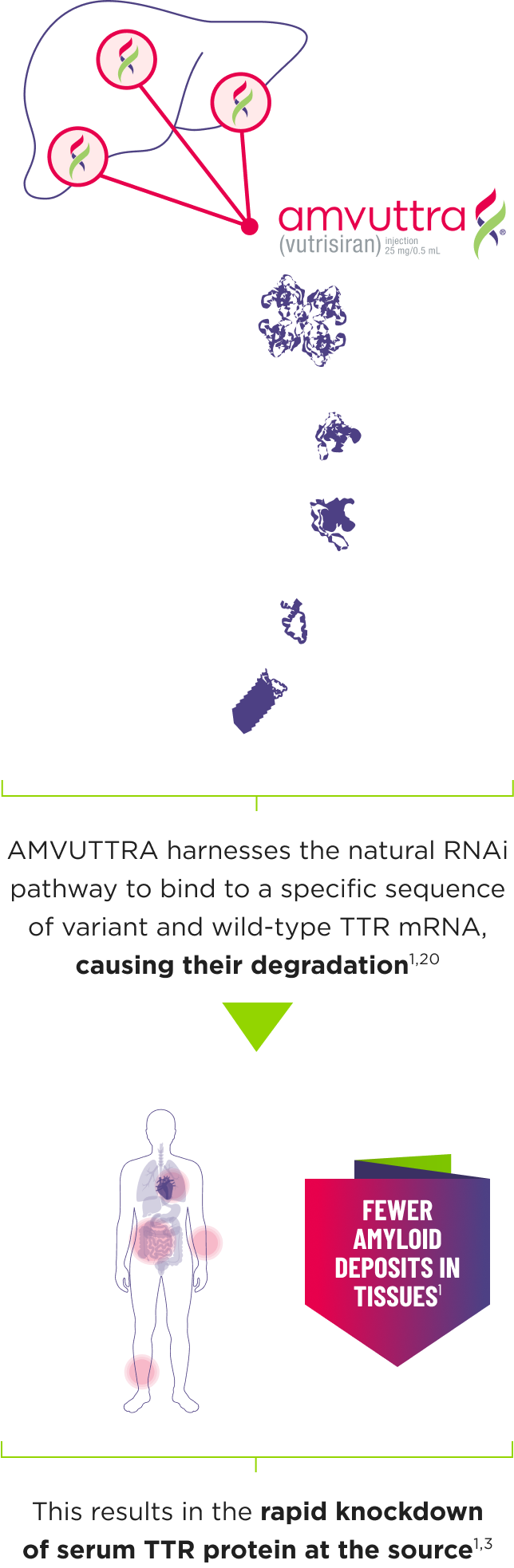
AMVUTTRA addresses the underlying cause of ATTR-CM and hATTR-PN with rapid knockdown of TTR1,3

Intervene early with AMVUTTRA, the first and only treatment approved for ATTR‑CM and hATTR‑PN1,21,22
- AMVUTTRA is formulated for targeted delivery to the liver, the primary source of TTR production1,2
- AMVUTTRA deploys the body’s natural silencing complex to act upstream of tetramer formation1,20
mRNA=messenger RNA; RNAi=ribonucleic acid interference; TTR=transthyretin.
AMVUTTRA delivered RAPID KNOCKDOWN of TTR as early as 6 weeks in HELIOS-B3,23*
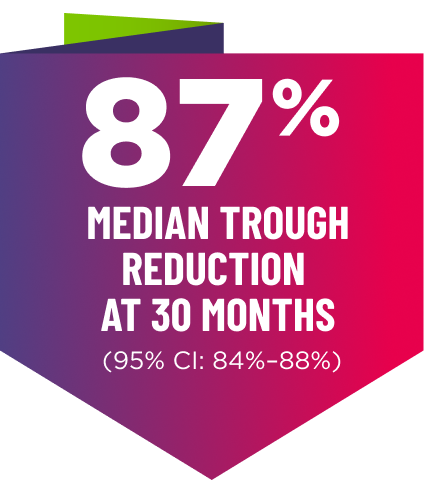
Knockdown of TTR was sustained through 30 months23†‡
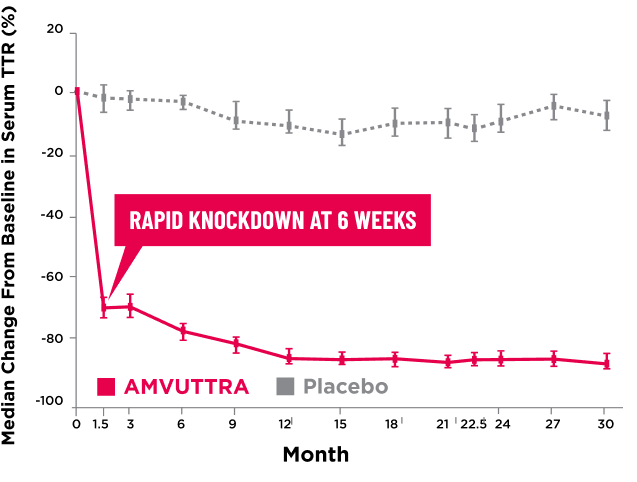
Knockdown of TTR was sustained through 30 months23†‡
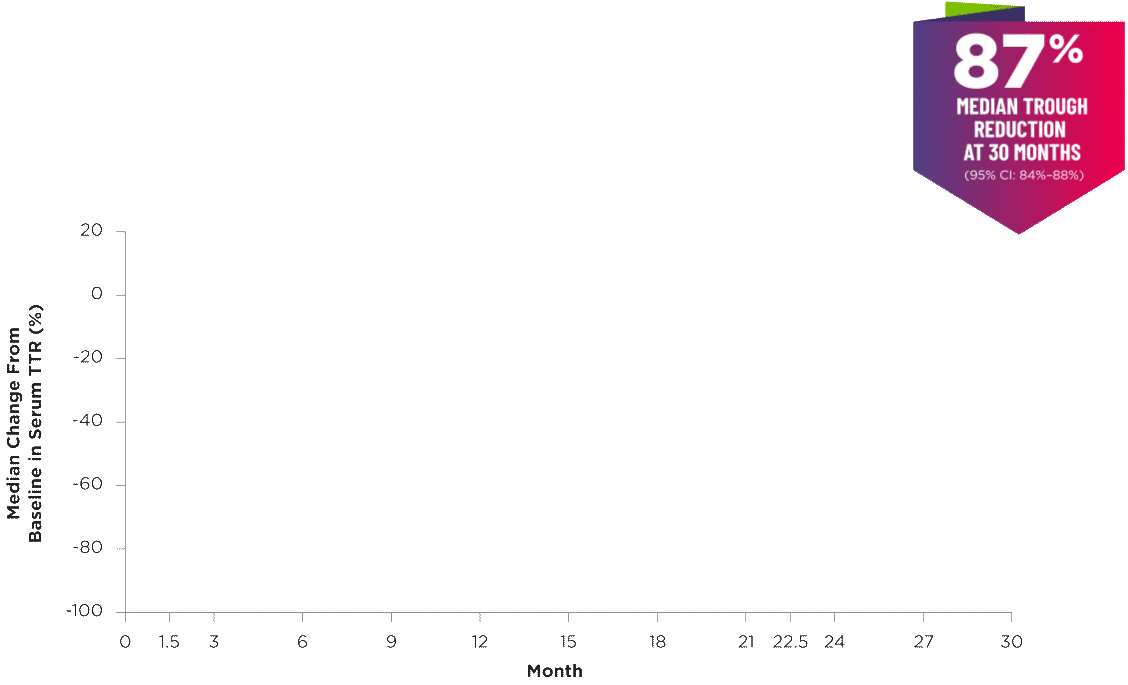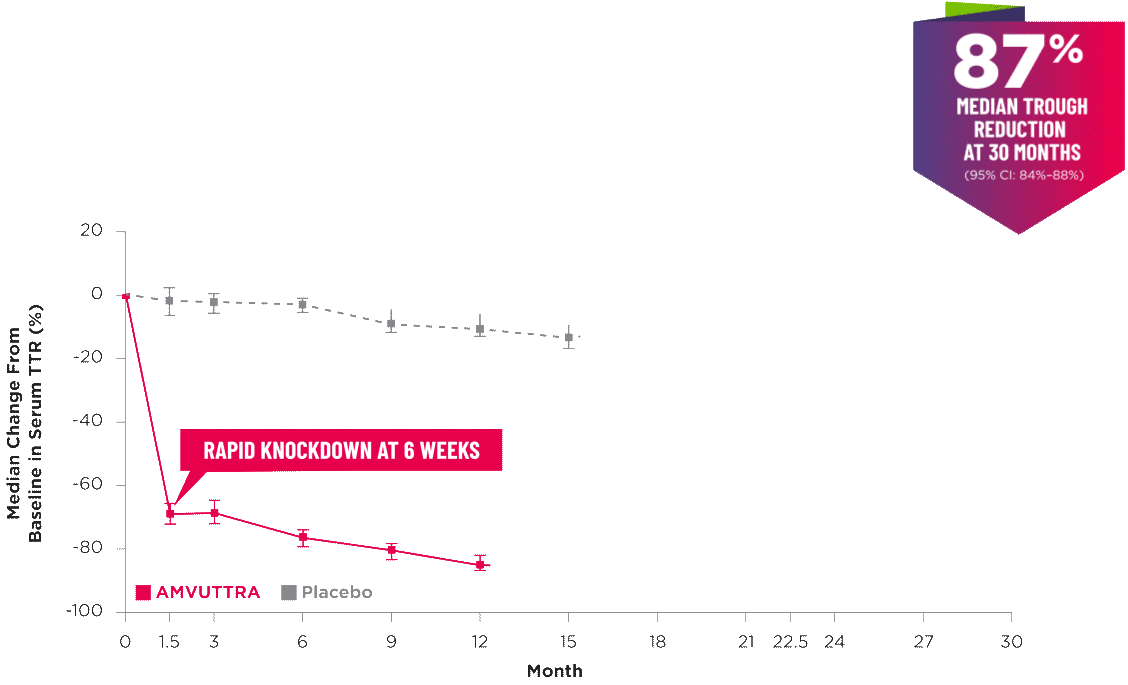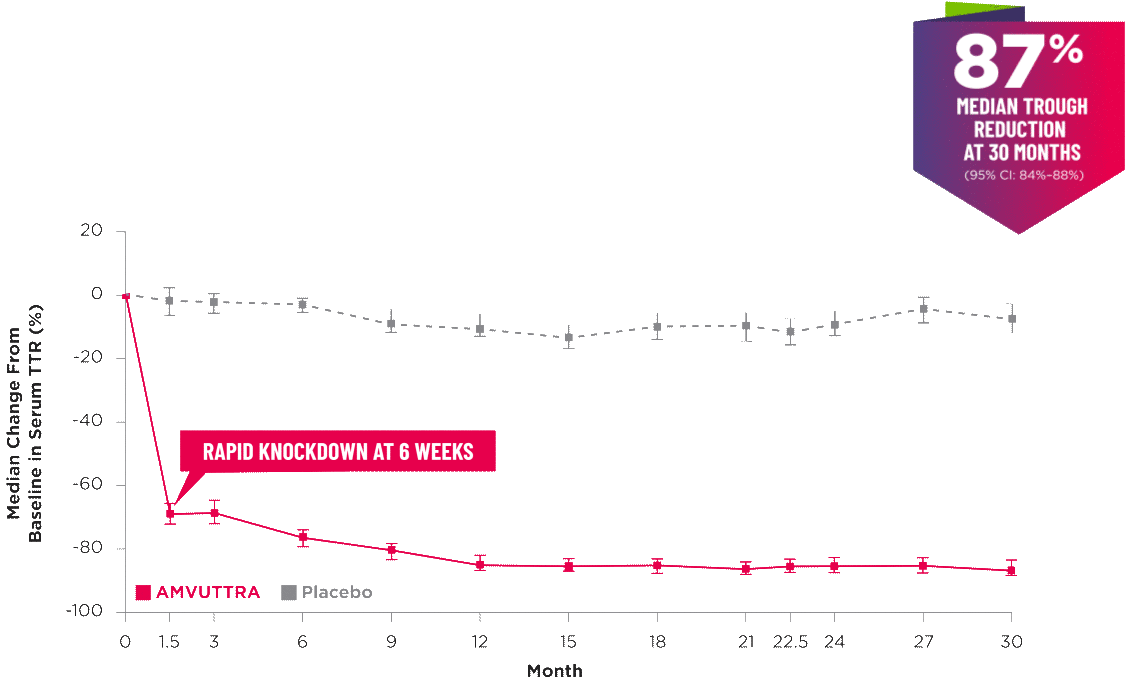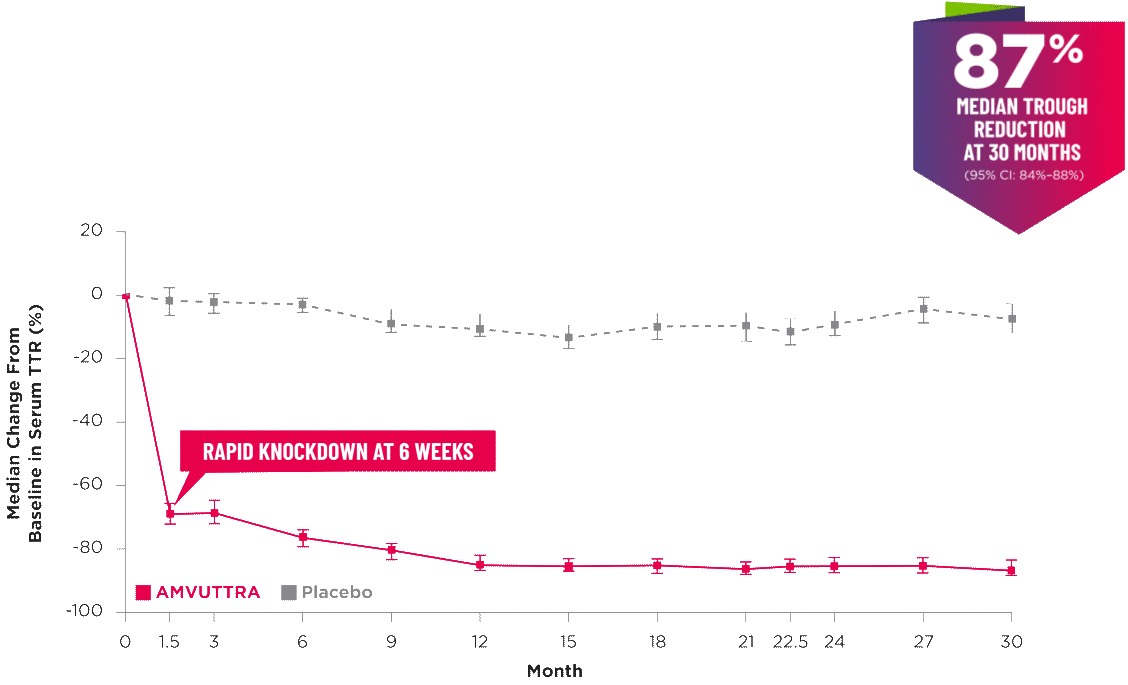
- In the HELIOS-B pivotal trial, serum TTR was evaluated in patients with ATTR-CM treated with 25 mg of AMVUTTRA via subcutaneous injection once every 3 months1
- A similar reduction in TTR levels was observed regardless of baseline tafamidis use, disease type (wtATTR or hATTR), sex, age, weight, or race1
*TTR knockdown was first measured in the serum at 6 weeks in HELIOS-B. 23
†TTR knockdown level is demonstrated through serum TTR reduction. 1
‡Bars indicate 95% confidence intervals. 23
CI=confidence interval; hATTR=hereditary ATTR; TTR=transthyretin; wtATTR=wild-type ATTR.
AMVUTTRA achieves sustained knockdown of TTR with a subcutaneous injection 4 times per year.1
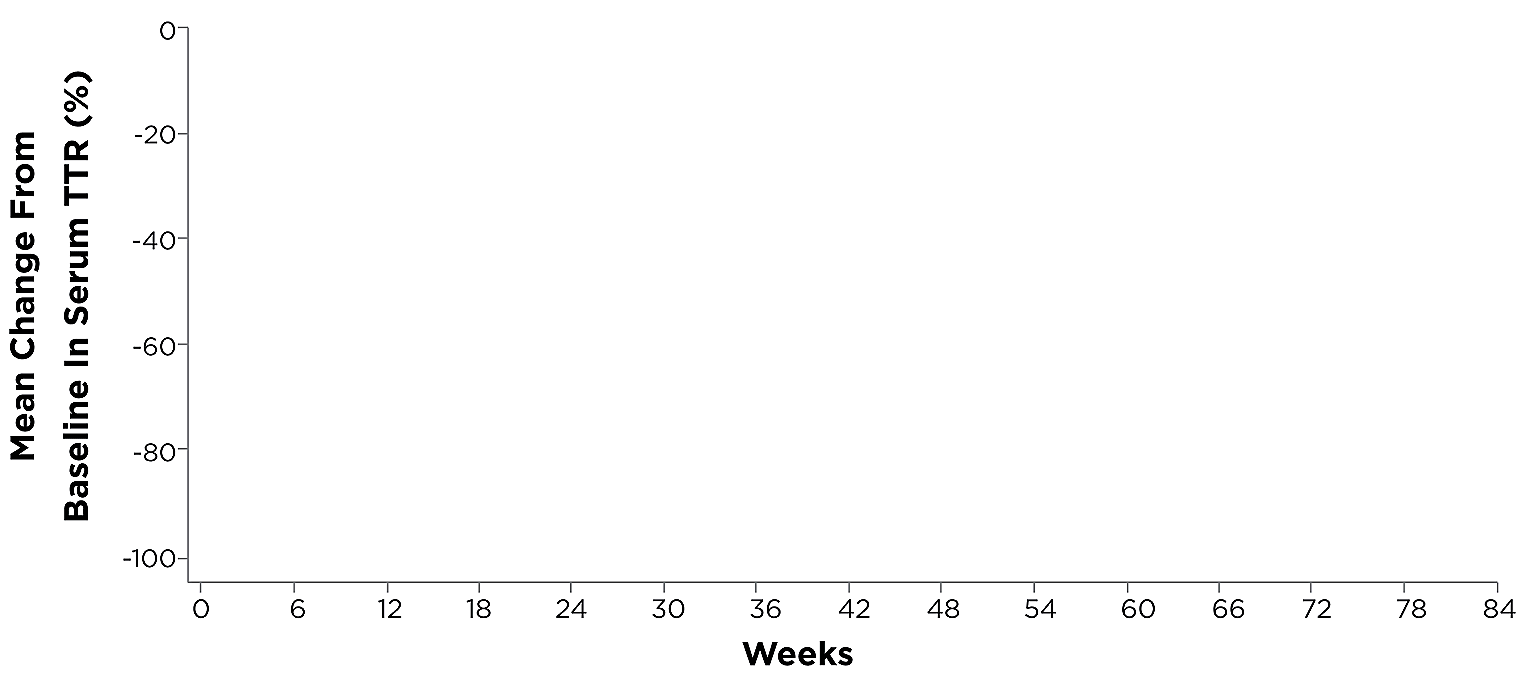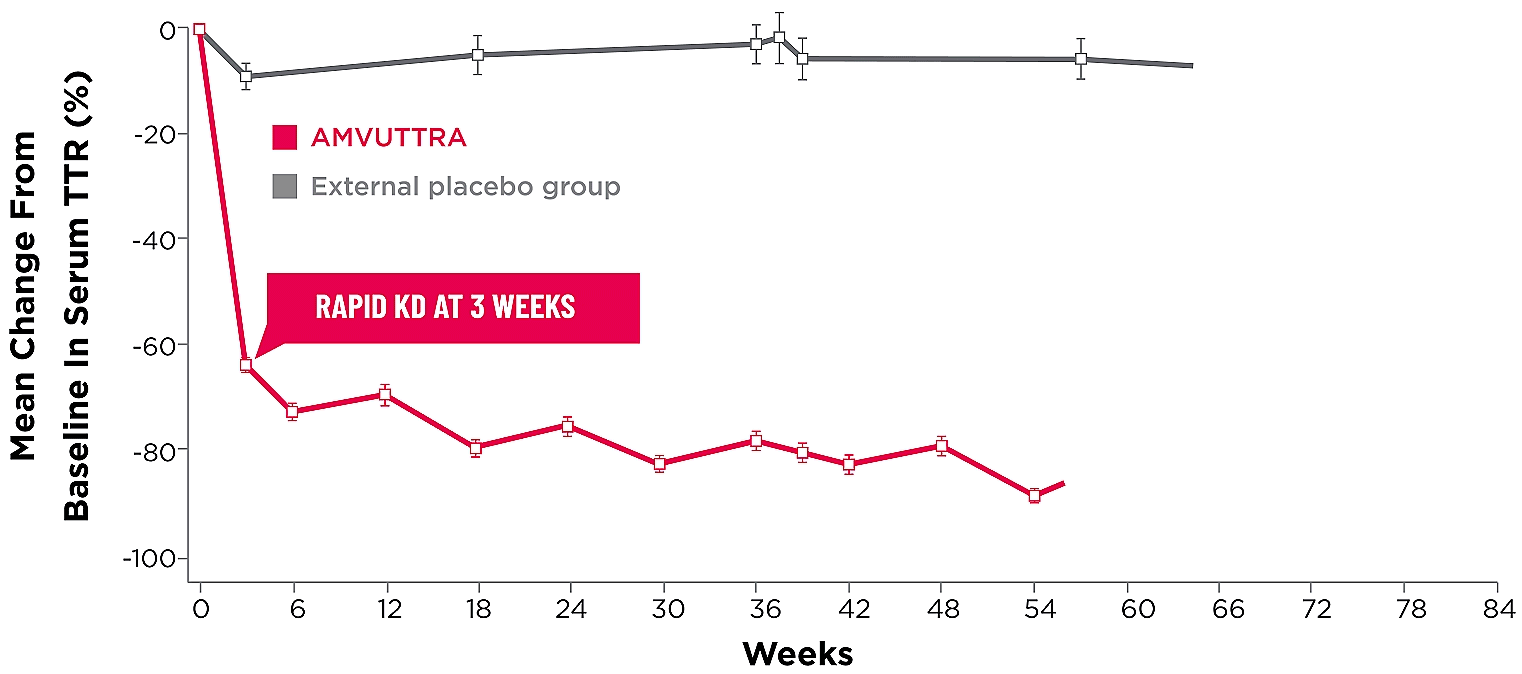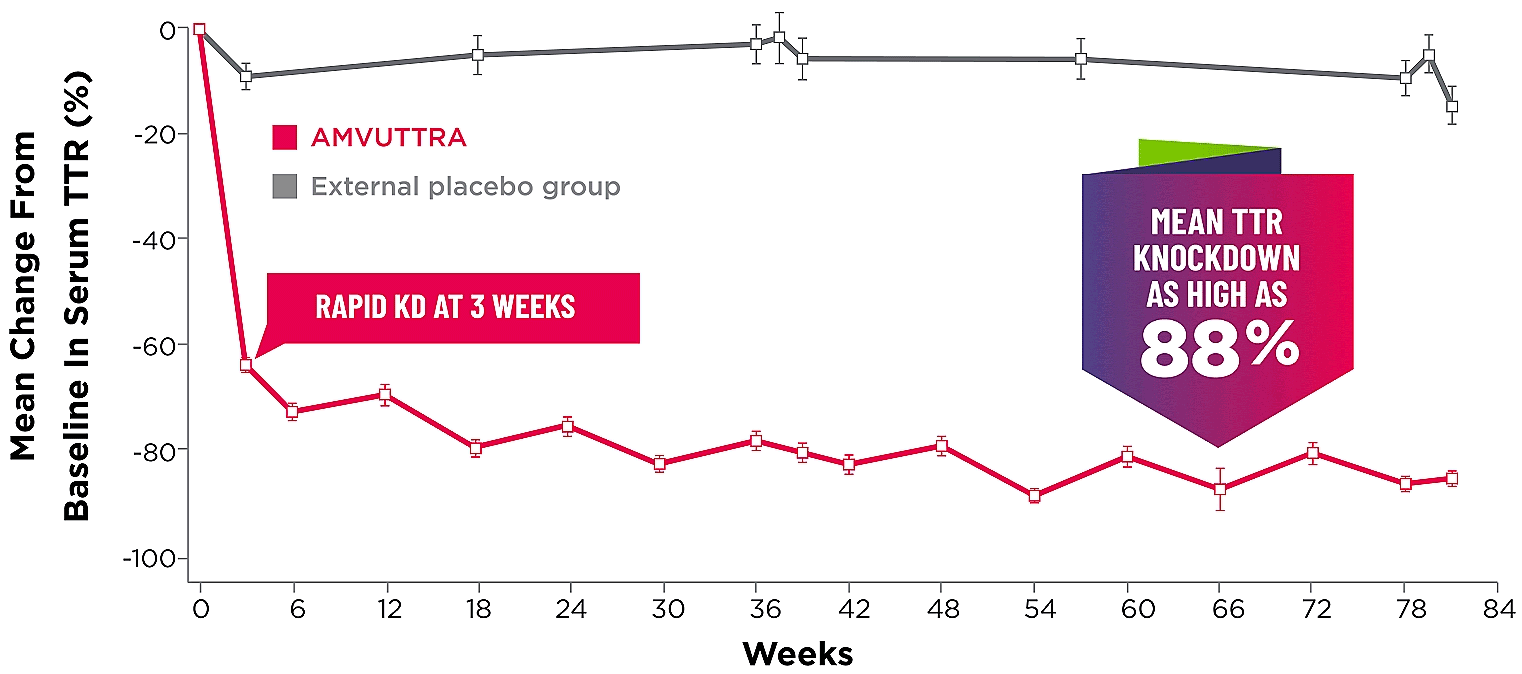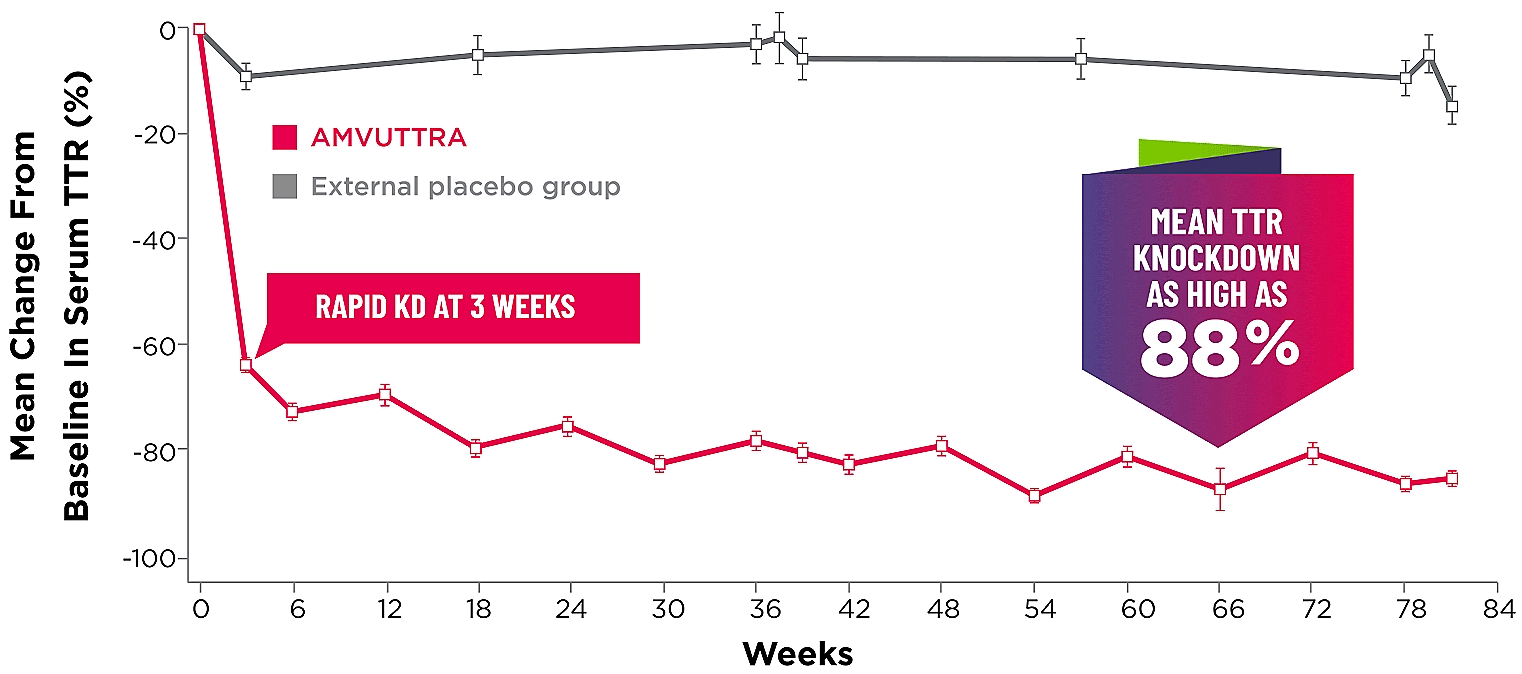
Treatment with AMVUTTRA led to rapid knockdown of TTR as early as 3 weeks in HELIOS-A24*
Knockdown of TTR was sustained over 18 months24,25†‡
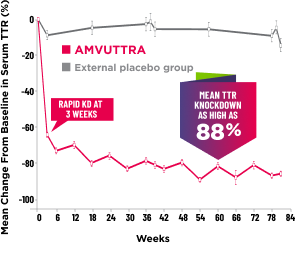
Knockdown of TTR was sustained over 18 months24,25,b,c
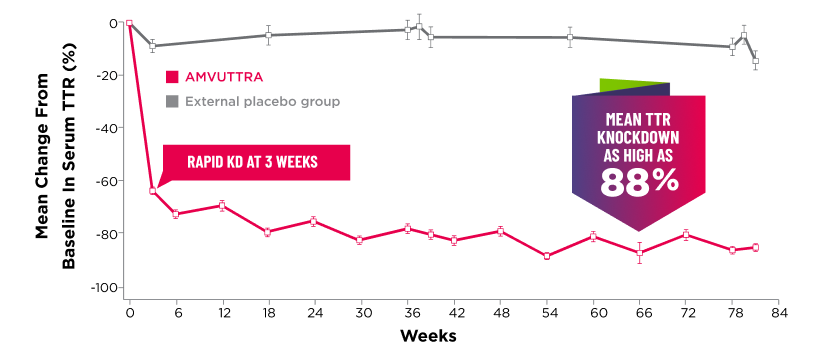
*First measured at 3 weeks.
†Bars represent SEM.
‡TTR knockdown level is demonstrated through serum TTR reduction.
KD=knockdown; SEM=standard error of the mean.
- Serum TTR was evaluated in patients with hATTR-PN treated with 25 mg AMVUTTRA via subcutaneous injection once every 3 months1
- With AMVUTTRA, similar rapid knockdown in serum TTR was observed regardless of V30M variant status, previous TTR stabilizer use, sex, age, weight, or race1,23