HELIOS-A Efficacy

*Mean mNIS+7 at baseline was 60.6 with AMVUTTRA and 74.6 with external placebo group.1,2
†Bars represent SEM.
‡N=number of evaluable patients.
§LS mean difference -28.6 (95% CI: -34.0, -23.1).2
CI=confidence interval; LS=least squares; SEM=standard error of the mean.
48% of patients treated with AMVUTTRA experienced reversal in neuropathy impairment from baseline2*†‡
Exploratory Analysis
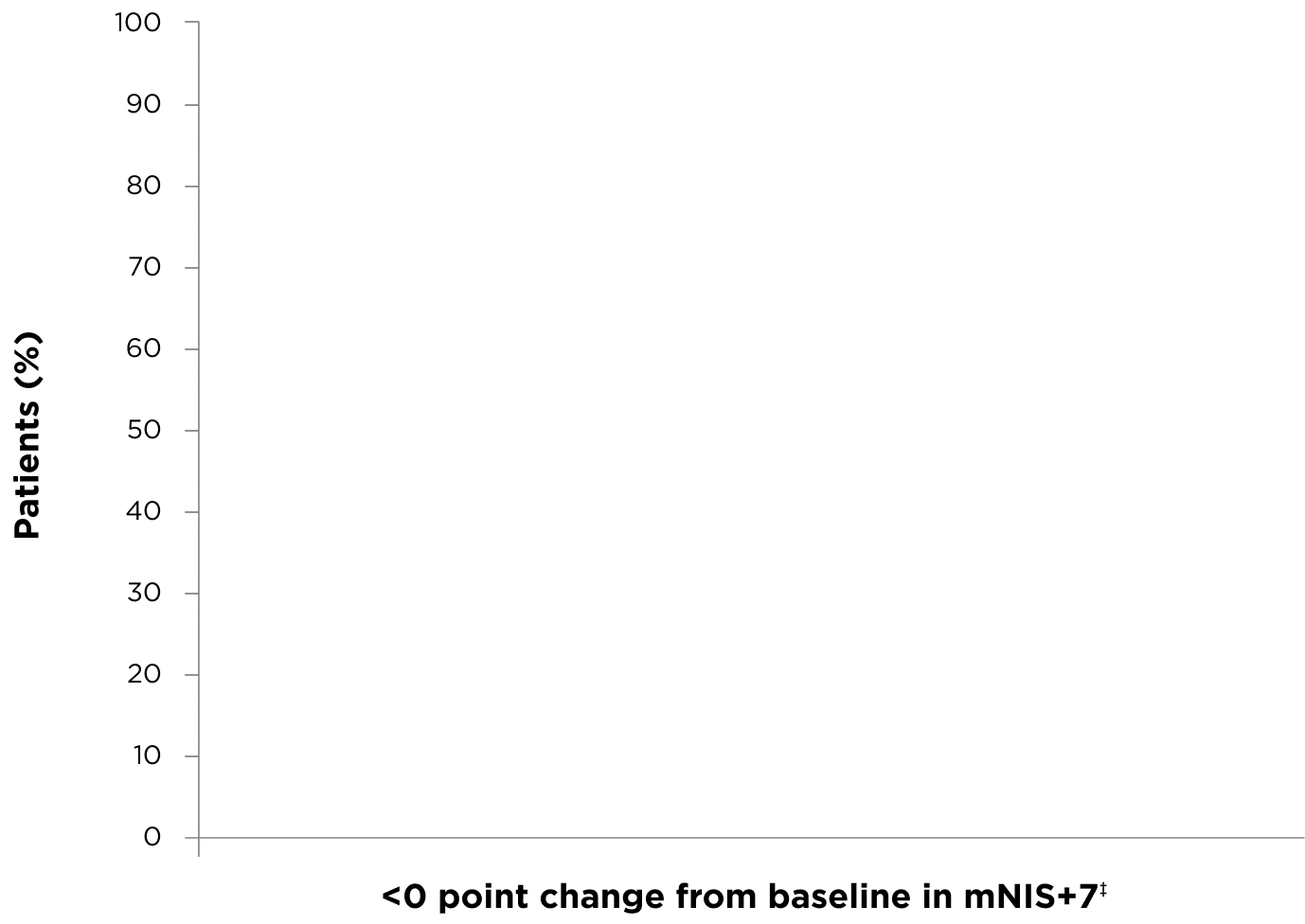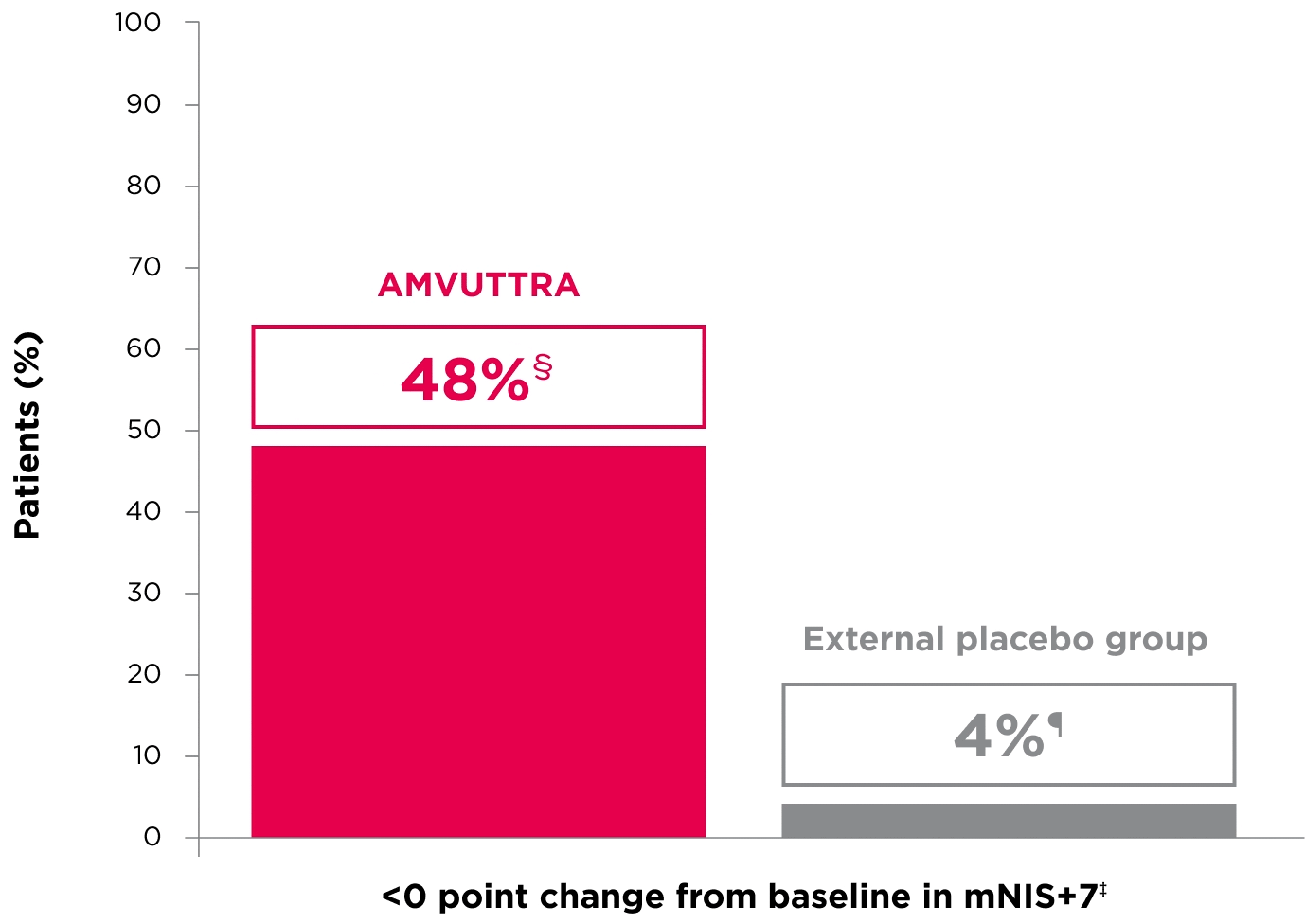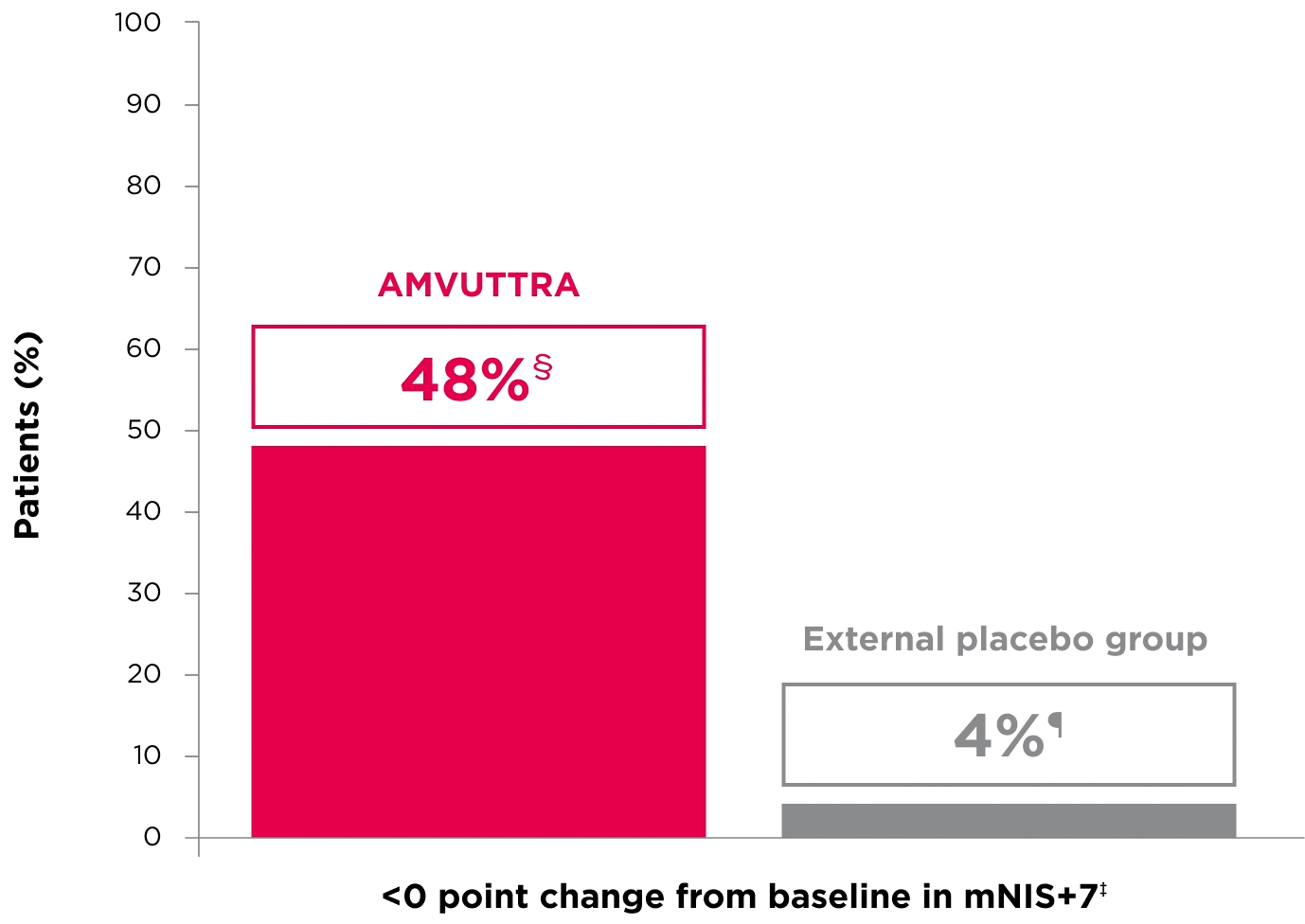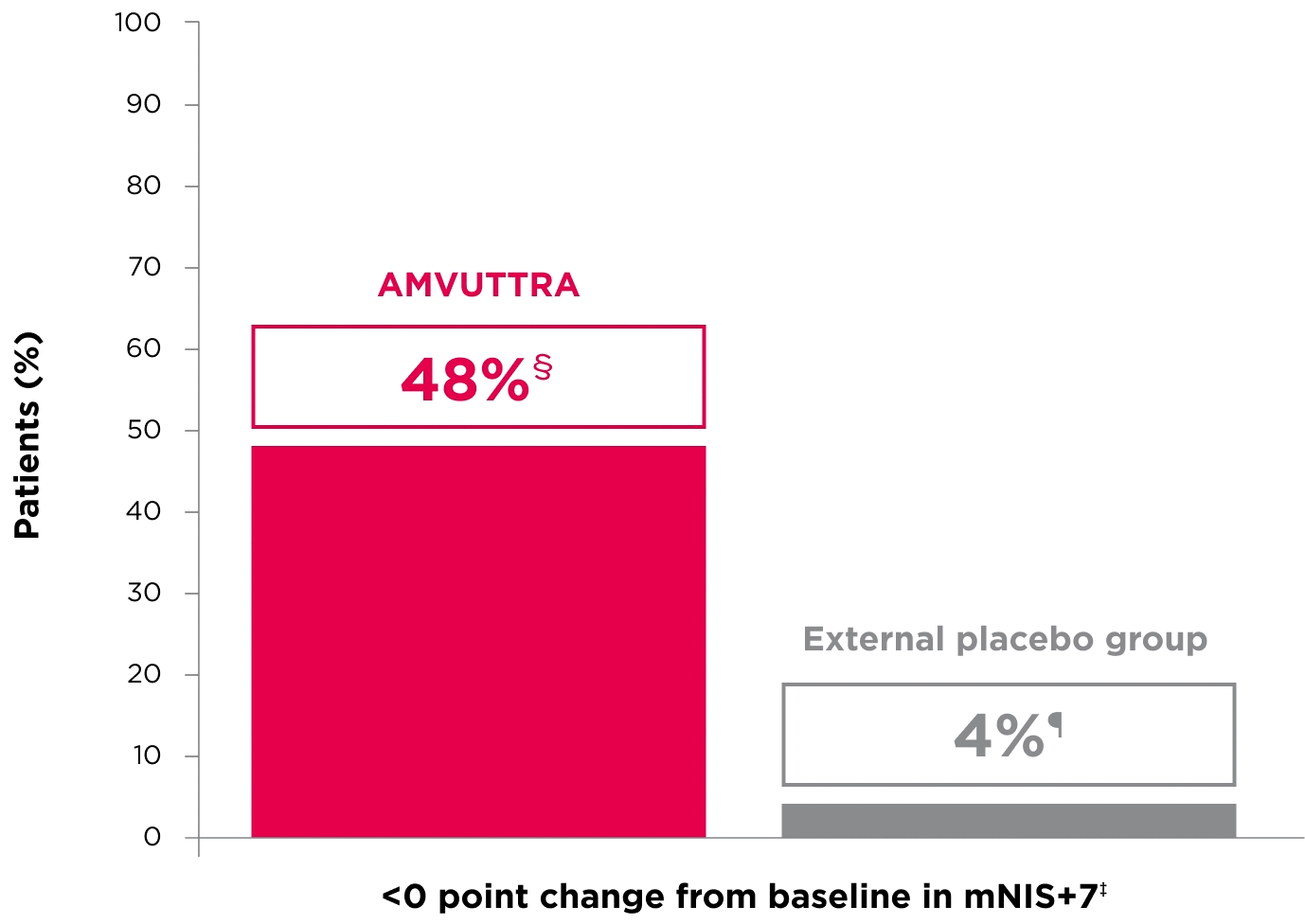
*Odds ratio: 22.9 (6.8, 76.9); nominal p-value.2
†Percentages based on mITT population: AMVUTTRA (n=118); external placebo group (n=77).2
‡Reversal defined as mNIS+7 change from baseline of <0 points.2
§95% CI: 39.3, 57.3.2
¶95% CI: 0.0, 8.2.2
mITT=modified intention-to-treat.

AMVUTTRA significantly improved quality of life1,2

*Norfolk QoL-DN scores at baseline were 47.1 with AMVUTTRA and 55.5 with external placebo group.1,2
†Bars represent SEM.
‡N=number of evaluable patients.
§LS mean difference -21.0 (95% CI: -27.1, -14.9).2
AMVUTTRA improved nutritional status2
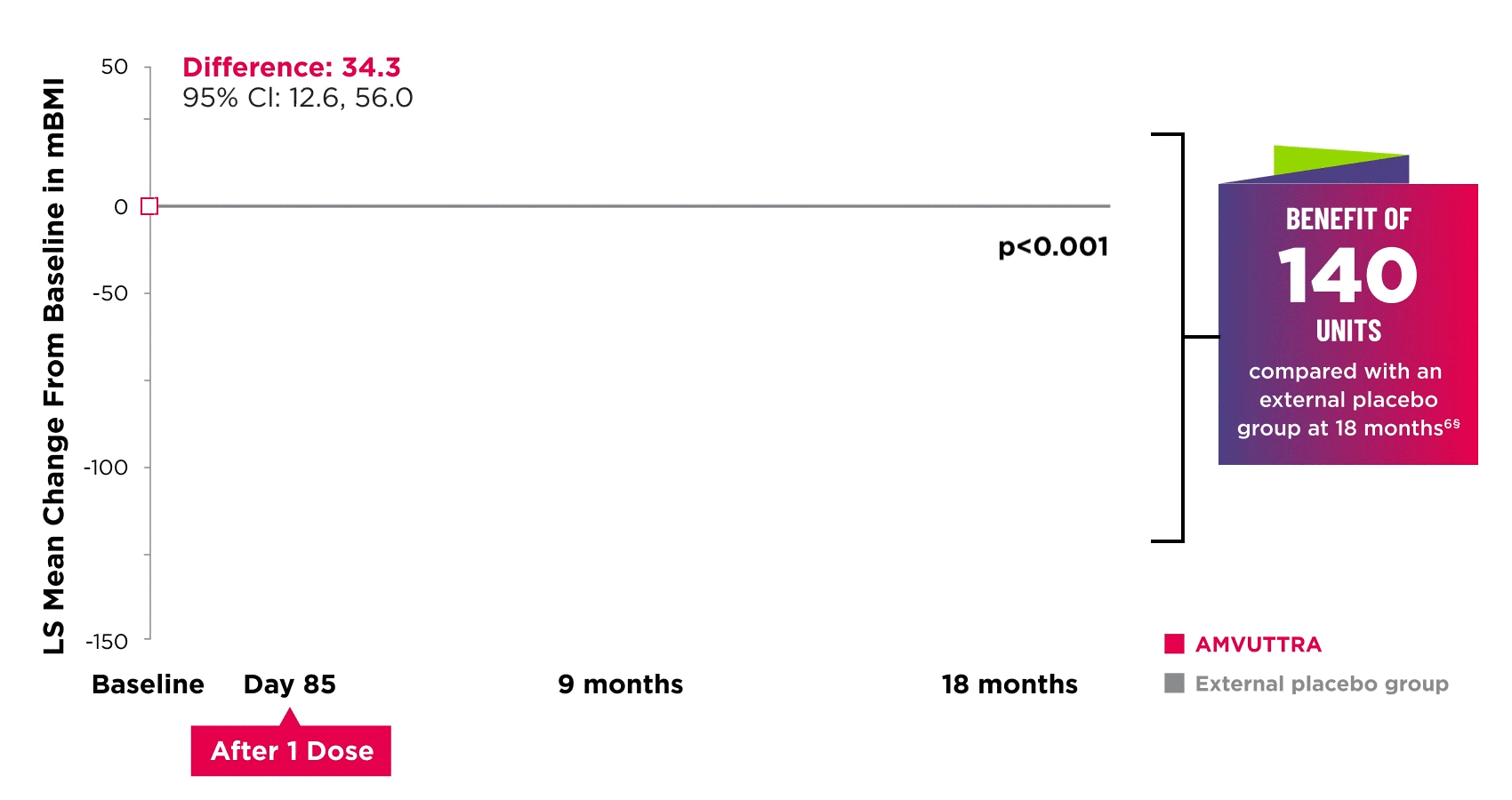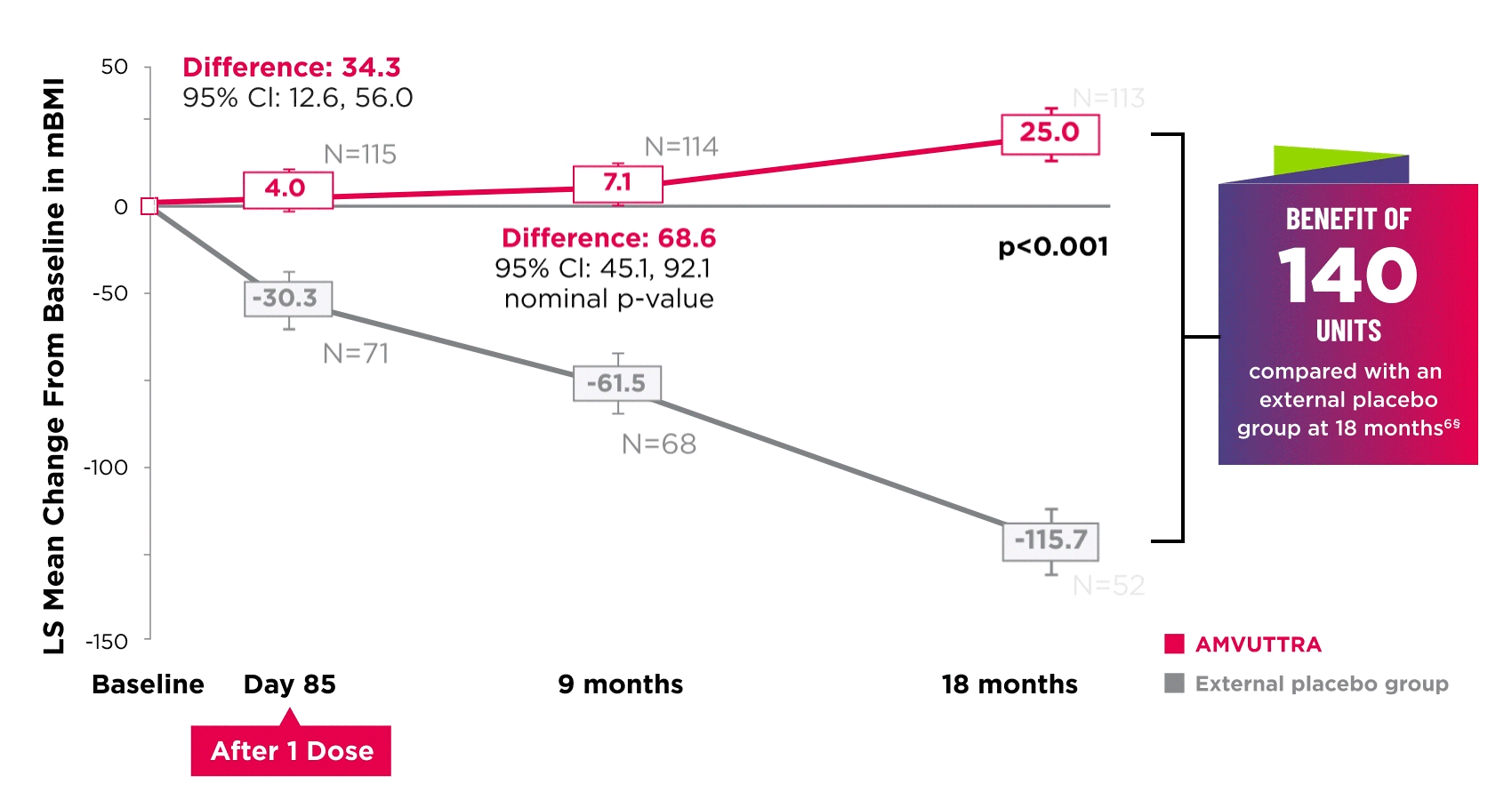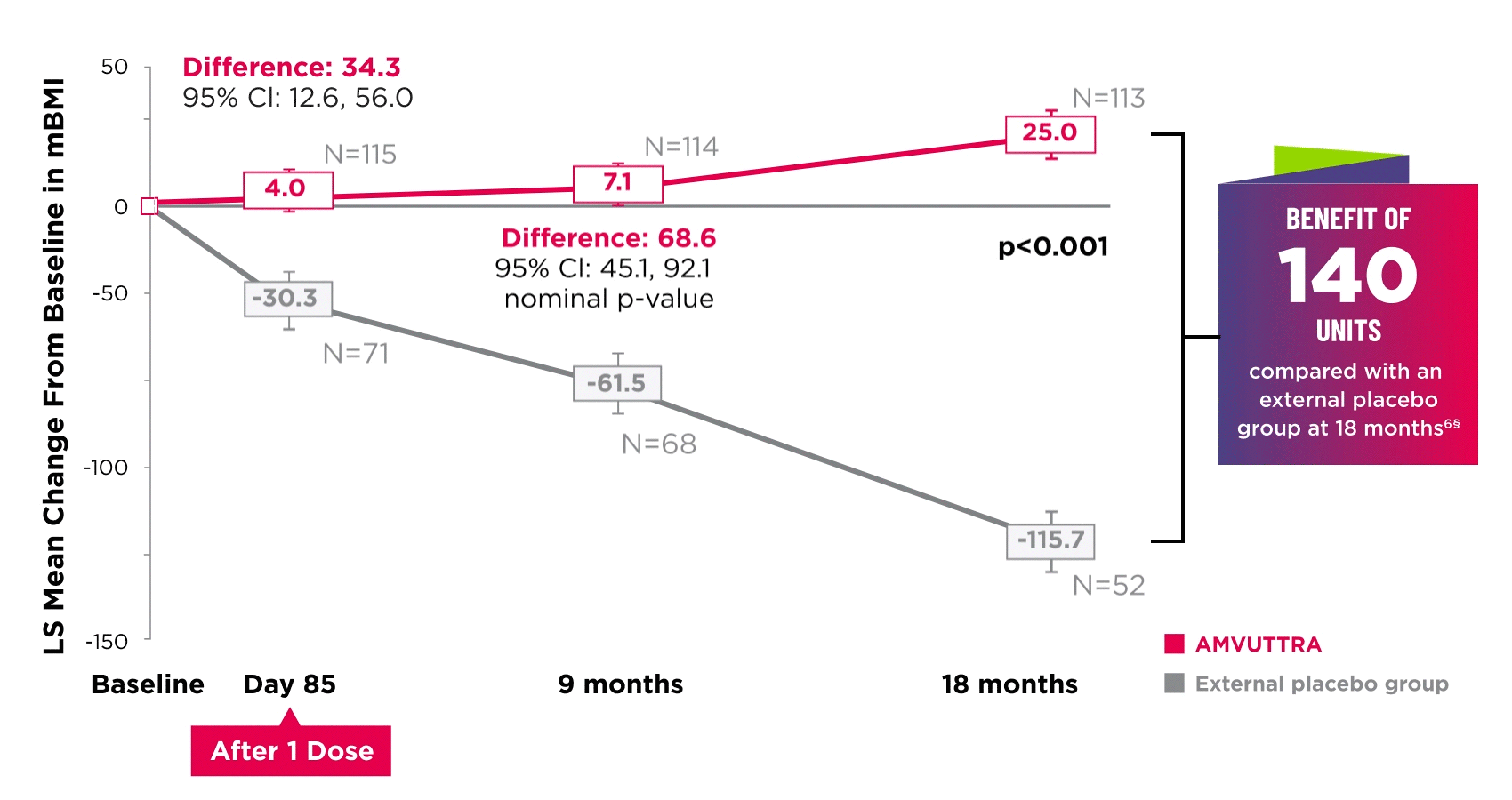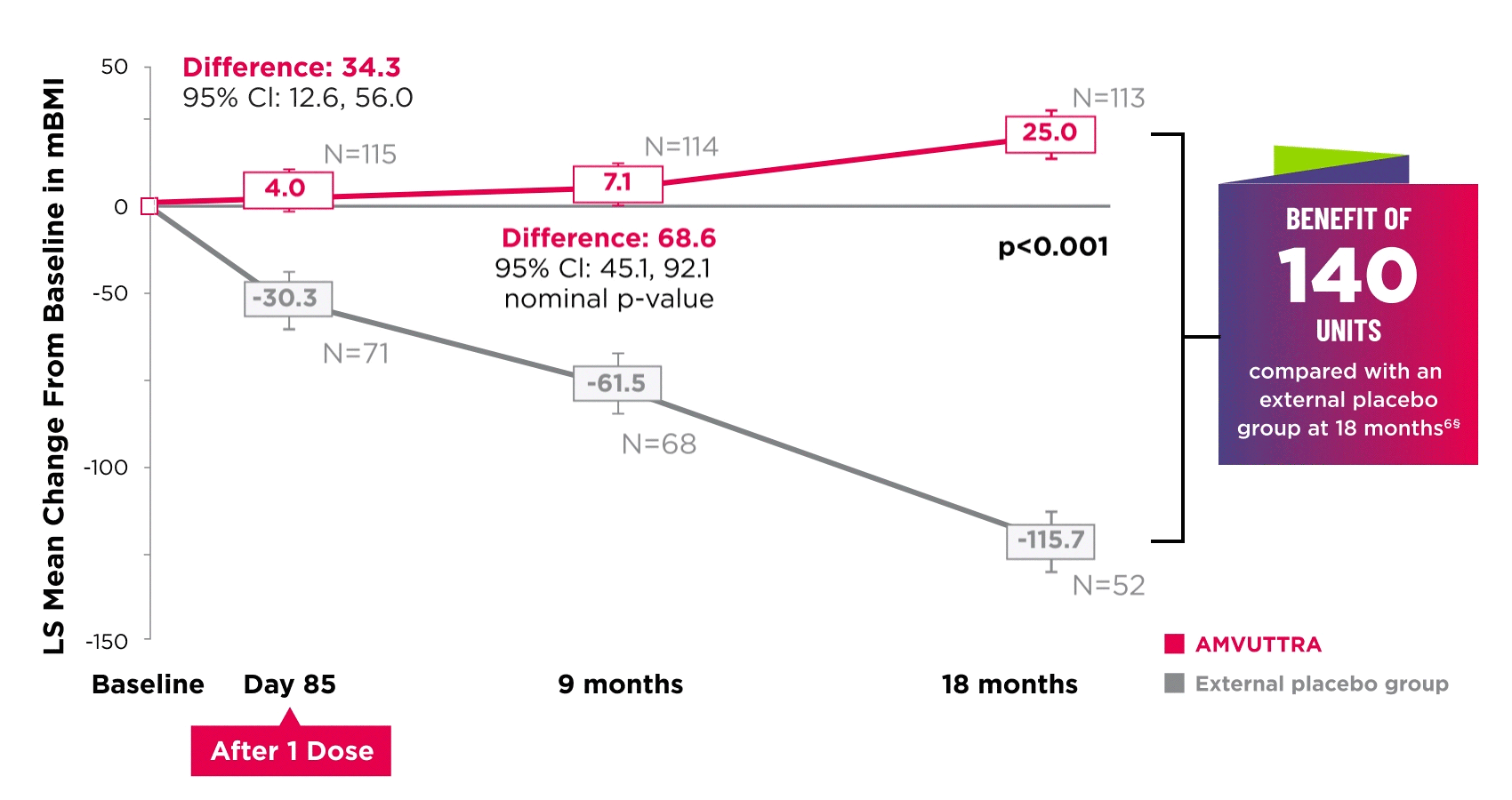

*Mean mBMI at baseline was 1057.4 with AMVUTTRA and 989.9 with external placebo group.6
†Bars represent SEM.
‡N=number of evaluable patients.
§LS mean difference 140.7 (95% Cl: 108.4, 172.9).6
AMVUTTRA improved other key measures of disease burden



- Validated composite measure of motor, sensory, and autonomic neuropathy, with a score ranging from 0 (no impairment) to 304 points, with higher scores representing a greater severity of disease
- Activities of daily living
- Polyneuropathy symptoms
- Autonomic function
- Small fiber nerve function
- Physical functioning/large fiber nerve function
- Nutritional status assessment based on body mass index and serum albumin (kg/m2 x albumin [g/L])
- Higher score indicates better nutritional status
- mBMI is used as a tool to monitor disease progression and provide prognostic information, showing close correlation with duration of gastrointestinal disturbances, malabsorption, and functional capacity
- Measure of gait speed (m/sec)
- A higher number indicates less disability/less impairment
- 24-item scale that evaluated patient-reported ability to perform activities of daily living such as eating, bathing, dressing, and standing
- Score ranges from 0 to 48; higher score indicates less disability







