HELIOS-B Clinical Trial
HELIOS-B was a landmark clinical trial establishing the efficacy and safety of AMVUTTRA® in ATTR-CM1
A global, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, Phase 3 study1-3

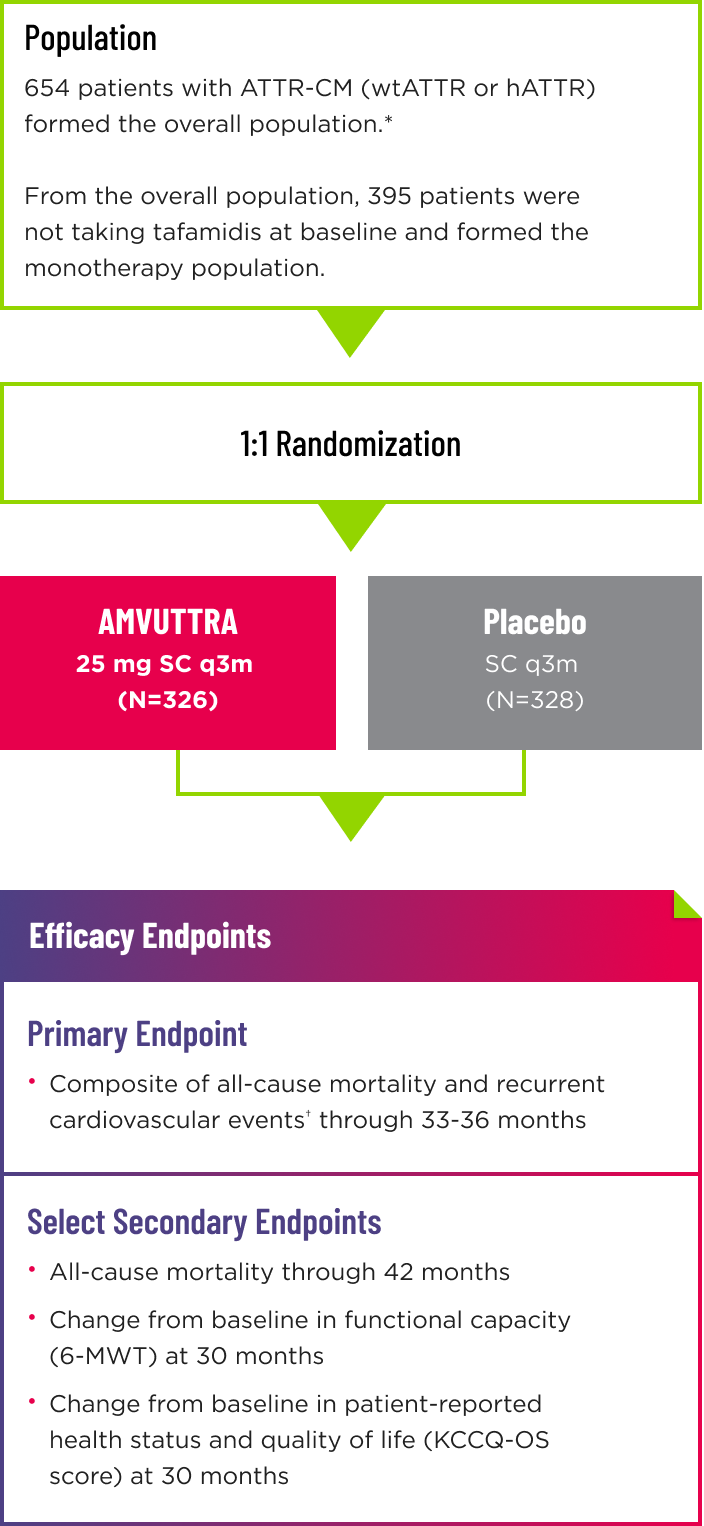
- Following the double-blind (DB) period of up to 36 months, patients on placebo were eligible to transition to AMVUTTRA in the open-label extension, which lasted up to 24 months2
- Randomization was stratified according to tafamidis use at baseline (with vs without), ATTR disease type (hereditary vs wild-type), and NYHA class and age at baseline (NYHA class I or II and age <75 years vs all others)1
*The overall population included patient cohorts with and without tafamidis use at baseline.1
†Cardiovascular events are defined as hospitalizations for cardiovascular causes or urgent visits for heart failure.1
6-MWT=6-minute walk test; ATTR=transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis; ATTR-CM=cardiomyopathy of transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis; hATTR=hereditary ATTR; mg=milligram; KCCQ‑OS=Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire-Overall Summary; NT-proBNP=N-terminal prohormone of brain‑type natriuretic peptide; NYHA=New York Heart Association; q3m=every 3 months; SC=subcutaneous; wtATTR=wild-type ATTR.
One of the largest studies with a contemporary population of patients with ATTR-CM2,4,5*
HELIOS-B enrolled a population representative of present-day patients with ATTR-CM, characterized by2,3:
- Earlier diagnoses
- Less severe disease
- Increased heart-failure management
- Concomitant ATTR-CM medication
- Use of background HF medications and concomitant ATTR-CM therapy was similar across the AMVUTTRA and placebo study arms2
- SGLT2 inhibitors were added to HF guidelines in 2022, reinforcing their role as a standard of care in treatment of patients with HF6
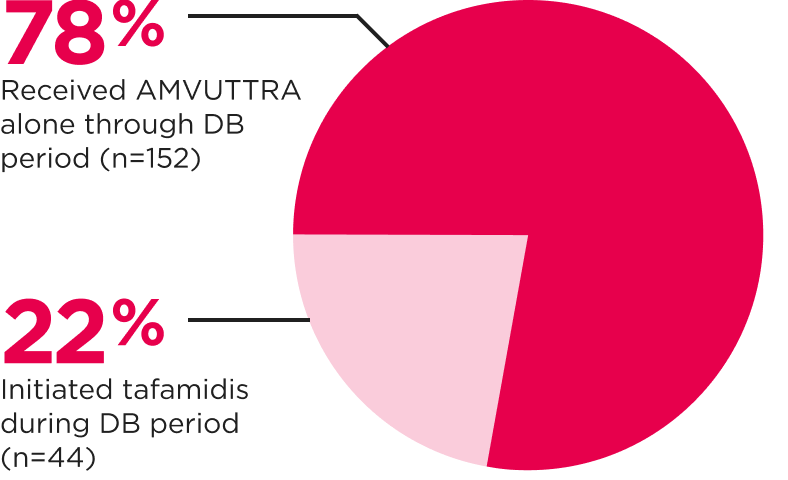
The monotherapy population comprised ~60% of patients in HELIOS-B1,2
AMVUTTRA Monotherapy (n=196)3

Placebo Monotherapy (n=199)3
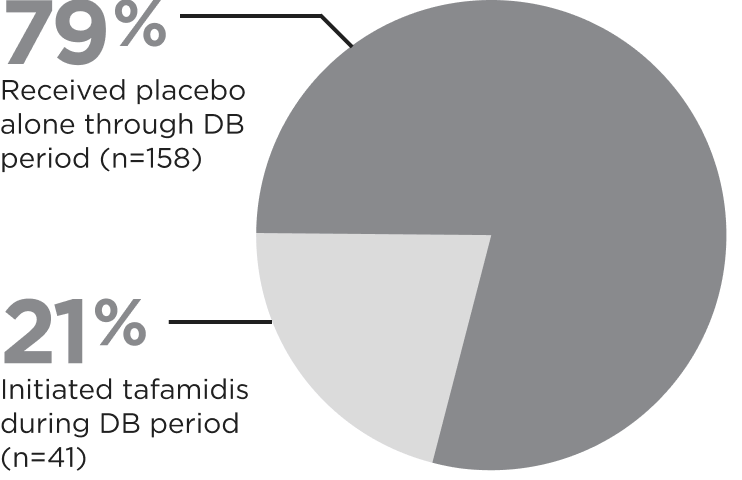

The study population was typical of present-day patients with ATTR-CM2





